Dear Friends,
It can be hard to maintain optimism as fascism and climate disaster advance across the globe, including in the US. But then we’re reminded that those who must fight back, do fight back—and claim victories. As we publish, word arrives that 309,000 “unauthorized” migrants from Haiti have gained extension and reauthorization of Temporary Protected Status, allowing them to remain in the US until at least 2026. In another cause for hope, our newsletter celebrates the naming of an impressive new leadership team at Adhikaar, a local social justice organization for Nepali-speaking immigrants. Our second article describes a cynical, two-sided approach to migration recently announced by the Biden administration. The new approach channels Trump’s racist cruelty on border policy. But it also establishes a new pathway to legal status for undocumented spouses that immigrant justice activists have demanded for years. Can we find a way to stitch our multiple justice battles and partial victories together into a powerful resistance?
1. New Leaders at Adhikaar
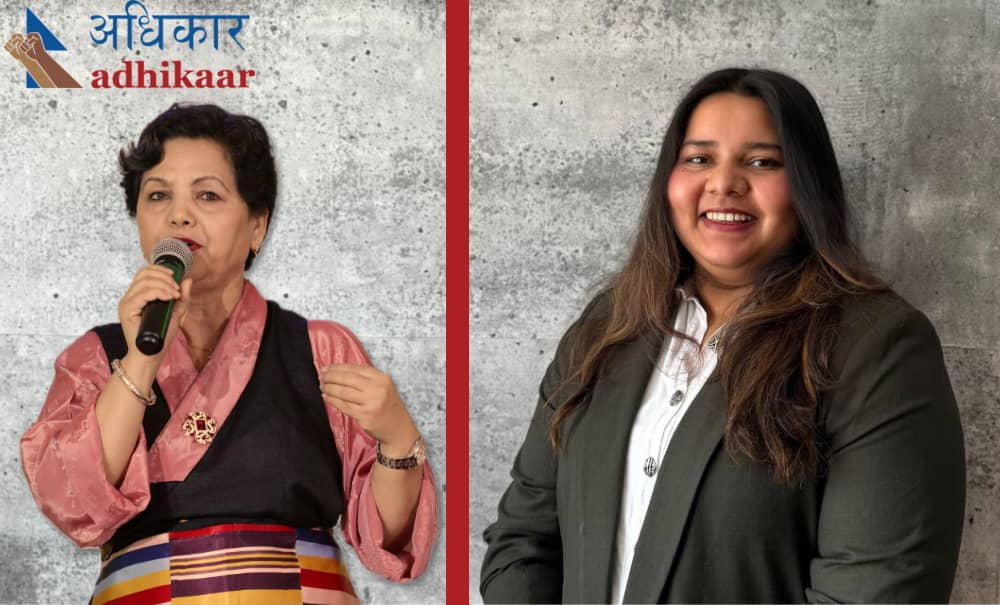
Last November, Adhikaar, a leading social justice advocate for Nepali-speaking immigrants and refugees, announced that it would hire two Co-Executive Directors to replace long-time Executive Director Pabitra Benjamin. The organization has now completed its search, choosing two activists with impressive backgrounds.
Narbada Chhetri was appointed the first Co-Executive Director in November 2023 and fully assumed her role on April 1 of this year. Narbada was a human rights activist in Nepal for 15 years before she came to the United States. She joined Adhikaar in 2007 as an organizer, and at the time of her appointment was Director of Organizing and Programs. She has been a fierce advocate of rights for Nepali-speaking communities, successfully organizing and campaigning for passage of the NY State Domestic Workers Bill of Rights and the NY State Nail Salon Workers Bill of Rights. She will focus on Programs.
As announced in an email to supporters, the search for a second Co-Executive Director ended on June 18 with the appointment of Cynthia Saxena to focus on Adhikaar’s infrastructure. Cynthia’s background includes work with both large organizations and grassroots NGOs. She has mobilized resources and nurtured growth for non-profits, small enterprises and UN agencies. She has extensive experience developing strategic partnerships, fundraising and international relations.
JHISN congratulates Narbada Chhetri, Cynthia Saxena and Adhikaar, and wishes them continued success!
WHAT CAN WE DO?
- Donate to Adhikaar, or follow them on social media.
- Read about Adhikaar’s campaigns and accomplishments.
2. Pain for Some, Hope for Others: Biden’s New Immigration Policies
In a transparent effort to defuse the issue of immigration during an election year, President Biden announced two major policy initiatives, backed by executive orders, in June. The first initiative drastically reduces the number of asylum seekers allowed to cross into the US. This is Biden’s response to the “out of control border crisis” being weaponized against him by the anti-immigrant Right. The second initiative, an extension of “parole in place,” could make it significantly easier for many undocumented spouses of US citizens to get green cards. This is a last-minute concession to immigrant families and progressive voters.
By simultaneously promoting tough border enforcement and family unification for long-established migrants, Biden hopes to mollify critics to his right and left, managing the volatile politics of immigration that imperils his reelection. But beyond electioneering, these initiatives will have a major impact—good and bad—on the lives of hundreds of thousands of migrants.
In the case of asylum seekers, the impact is very bad indeed. Biden has employed the same legal argument Trump used for his “Muslim ban” in order to impose a restrictive cap on the number of asylum seekers allowed to stay in the US. The administration says that anyone claiming asylum without prior permission to enter has “illegally” crossed the border, and is therefore subject to deportation at the discretion of the US government. This is a direct violation of the letter and spirit of humanitarian laws passed after the horrors of World War II. Those laws—national and international—specify that anybody on US soil has the right to request asylum, no matter how they arrived.
Biden argues that he has no choice, since there is chaos on the border and the Republicans refuse to make a deal on border legislation. He also points out that the cap has exceptions for victims of human trafficking and unaccompanied minors. But the reality is that on his watch, thousands of asylum seekers a week are now illegally returned to Mexico and other countries, blocked from making their legitimate claims, often after arduous struggles to reach the border.
Many Democratic politicians and civil rights groups denounce the asylum cap. The ACLU is one of the groups that have promised to fight it in court. They commented that Biden’s executive order “will severely restrict people’s legal right to seek asylum, putting tens of thousands of lives at risk.”
In stark contrast, Biden’s new “parole in place” expansion policy has been widely hailed by immigrant justice groups, some of whom claim it as a major victory achieved after years of organizing.
Current US law allows citizens to sponsor non-citizen spouses for permanent residency as long as they entered the US in an “approved” way. But in order for undocumented spouses to gain legal status, they must leave the US, go to a consulate in another country, and apply for an immigrant visa to return. This process can require the spouse to be away from their family for up to ten years. Even then, obtaining a visa is not guaranteed.
There is also a long-standing executive branch program called “humanitarian parole” which permits beneficiaries to temporarily enter or remain in the US for a specific time. When humanitarian parole is granted to people who are already inside the US, it is known as “parole in place.” That is, without leaving the country and their family, paroled people can receive a work permit and begin the process of receiving a green card.
What Biden announced on June 18 was a major extension of parole in place. The new program will allow eligible spouses and step-children of US citizens (theoretically up to 500,000 people) to receive temporary protections and work permits, enabling them to apply for lawful permanent resident status through their spouses or step-parents without risking years of separation from their families.
Applications for expanded parole in place are expected to become available later this summer. According to US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) parole will be granted for up to three years, at which time people will either have a pending or final adjustment application completed.
Exactly who will be eligible, the fee, and what kind of documentation will be needed is still to be determined by DHS. However, here are the announced requirements:
An undocumented person may be eligible if they
- Have never been admitted or paroled.
- Have been in the US since at least June 17, 2024.
- Were married to a US citizen on June 17, 2024, or have a parent who was married to a US citizen on June 17, 2024 (if the marriage occurred before their 18th birthday and they are currently under 21 and unmarried).
- Do not pose a “threat to public safety or national security.”
- Convince DHS to exercise discretion in their favor.
Make the Road New York (MTRNY) has expressed cautious optimism about the new program. They point out that DHS has yet to publish the full details of eligibility, including who DHS believes poses “a threat to public safety or national security.”
“While this is not enough, we believe this is a step in the right direction, and we will continue to fight for a path to citizenship for all the 11 million undocumented immigrants in this country.”—MTRNY
In solidarity and with collective care,
Jackson Heights Immigrant Solidarity Network (JHISN)
Follow @JHSolidarity on Facebook and Twitter and share this newsletter with friends, families, neighbors, networks, and colleagues so they can subscribe and receive news from JHISN.