Dear friends,
While it did not make many headlines this week, hundreds of excluded workers marched across the Manhattan Bridge on Monday, demanding the state budget fund unemployment assistance for all workers, including undocumented immigrants. Our first article also covers an under-reported story: the recent legal challenge to new city district maps that split the vibrant South Asian community in South Queens into three separate districts. Our second article takes a deeper look behind a news story on immigration that actually is—for the moment—getting lots of attention: the systematic labor exploitation of unaccompanied child migrants.
Newsletter highlights:
- New City Council maps disenfranchise Asians in Queens
- Child migrants funneled into exploitative jobs
1. Lawsuit Challenges City Council Redistricting
“Despite the protections of the NYC Charter and our warnings throughout the redistricting process, the council map carved up the community and muffled their voices, continuing our city’s painful history of dividing, marginalizing, and disenfranchising communities of color.”—Jerry Vattamala, Democracy Program Director of the AALDEF
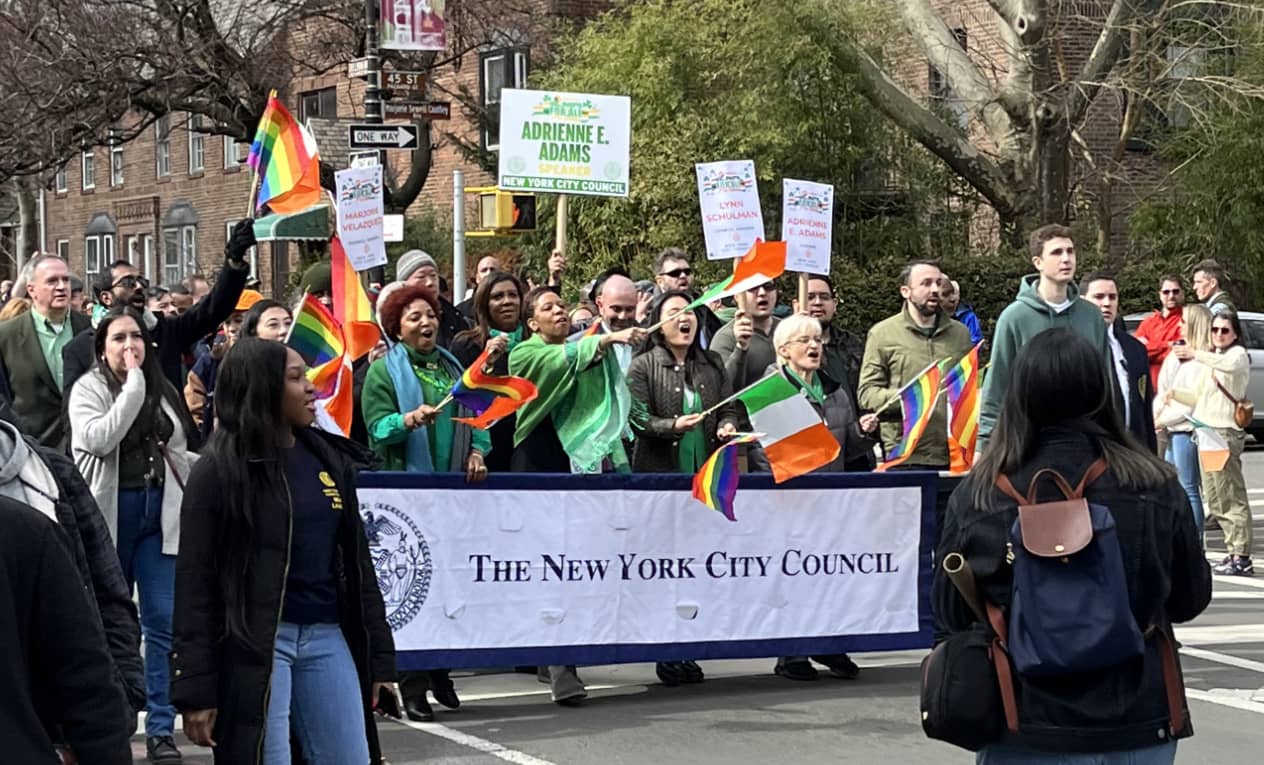
Last weekend, just before the petitioning process began for the NY City Council primaries in June, many Queens elected officials marched up Skillman Avenue in the St. Pats for All parade. Celebrating the inclusivity of Queens, they walked in the Sunnyside parade that was created 23 years ago in response to the St. Patrick’s Day parade in Manhattan refusing entry to LGBTQ+ marchers. Congresswoman Grace Meng reminded the Queens crowd in attendance that the Irish who came as refugees were not always welcomed with open arms, nor with equitable laws and policies. And Councilwoman Marjorie Velazquez raised cheers from the crowd as she said “Immigrants make America, America.”
The City Council electeds who were marching may have an additional hurdle to overcome this year: petitioning for the primaries may be delayed by a lawsuit brought by the Asian American Legal Defense and Education Fund (AALDEF) on behalf of South Asian community members including DRUM (Desis, Rising Up and Moving), our local immigrant workers’ organization. The lawsuit charges that 2022 redistricting decisions “unlawfully separat[ed] the Asian community” by carving up south Queens and “dilut[ing] the community’s voting strength.” The lawsuit calls for altered council maps that would create a new “opportunity district” for Asian American voters in the Queens areas of Richmond Hill and Ozone Park, and for a halt to petitioning until the district lines are settled. Judge Leslie Stroth ruled for a hearing last week and then recused herself from the case because she is also up for election as a candidate for the Supreme Court.
This lawsuit follows substantial debates, which began in November 2021, about redistricting maps that produced electoral districts that egregiously diminished the strength of Black, Asian, and Latino communities and voters. The New York City Charter says redistricting plans must ensure “the fair and effective representation of the racial and language minority groups in New York City,” protected by the 1965 United States Voting Rights Act. However, as Fulvia Vargas-De León, a lawyer with Latino Justice, noted, “Redistricting is often the silent voter suppressor.”
This is not a new issue. Thirty years ago a coalition was formed to create districts that accurately reflect demographic shifts in New York populations: the outcome was a set of “Unity Maps”. Many immigrant advocacy organizations, including the AALDEF, put their support behind the Unity Maps and presented them to the Independent Redistricting Commission (IRC) as examples of how redistricting could be non-partisan and be an accurate reflection of the minority populations in those areas. DRUM created a town hall series with the APA Voice (Asian Pacific American Voting and Organizing to Increase Civic Engagement), South Queens Women’s March, and the Caribbean Equality Project to oppose the redistricting that split the communities in Richmond Hill and Ozone Park. According to Patrick Stegemoeller, group attorney for the AALDEF, the Unity Maps were “ignored, in favor of a final plan that prioritized surrounding white-majority communities.”
This is not the first lawsuit for this election cycle: the Our City Our Vote law, allowing 800,000 eligible immigrants to vote in municipal elections, was passed by NYC voters in 2022. However, plaintiffs in Staten Island alleged the law was “adopted with impermissible racial intent.” They claimed Black citizen voters would be negatively impacted when more “Hispanic foreign citizens” vote: Justice Ralph Prozio of Staten Island agreed, and struck down the new law. The city is currently appealing that ruling and it is unlikely we will see that case resolved for the 2023 election cycle.
WHAT CAN WE DO?
- Know your own district: find it using an address & borough search.
- Stay up to date by receiving redistricting information from the Brennan Center’s newsletter.
- If you are able, financially support the work of the AALDEF and read the entire lawsuit petition.
2. Unaccompanied Migrant Children: Alone and Exploited
When the New York Times story about exploited migrant children dropped on February 2, it was a bombshell. The Times reported that in the past two years, 250,000 unaccompanied minors have entered the US; many of them are “ending up in dangerous jobs that violate labor laws—including in factories that make products for well-known brands.” Some work 12- or 14-hour shifts, while still trying to go to school. Dozens have been killed or seriously injured on the job. The heartbreaking Times article—based on interviews and stunning photography of more than 100 migrant child workers in 20 states—offered readers an emotional testament, and created a political sensation.
By the very next day, lawmakers in Congress were “clamoring for action.” The Department of Labor solemnly declared that it “takes these egregious violations very seriously and investigates every child labor complaint they receive and acts to hold employers accountable.” They promised a new “Interagency Taskforce to Combat Child Labor Exploitation” and a host of bureaucratic measures to beef up child protection and labor law enforcement policies.
It was as if the politicians didn’t know that exploitation of migrant children was happening. But as recently as last year, Reuters ran a series of articles about underage refugees working in the Hyundai-Kia supply chain and in poultry factories. And immigrant justice advocates have been urgently raising the predicament of young refugees for years. What the Times story accomplished was to give some of these oppressed children a face, and a voice. It forced the shameful treatment of unaccompanied minors into the mainstream of political discussion—at least temporarily.
From the point of view of immigrant justice, two issues stand out. The first is that the federal government, under Biden, is still separating children from their families at the southern border, although in new ways. By turning away almost all adult refugees under various cruel pretexts, in violation of international law, the US is forcing desperate refugee families to split up and send their children North alone—hoping that they can survive, and maybe help the family survive economically. This isn’t the openly racist carnival of the Trump years, which often targeted young children. It’s more of a cold-blooded unpublicized assembly line, trapping adult and infant refugees in war zones or fetid, dangerous encampments in Mexico, while rapidly processing tweens and teens to be sent all over the US.
The second issue is that the immigration system is effectively organized to funnel young asylum seekers into labor exploitation. The US government doesn’t just fail to provide these children with a basic income, legal representation, or services after they leave preliminary detention-–it doesn’t even know where many of them are. States and cities also do little to help. It is the volunteer sponsor-–often a distant relative or friend of a friend-–who is supposed to “provide for the physical and mental well-being of the child, including but not limited to, food, shelter, clothing, education, medical care and other services as needed.” But this isn’t realistic. As the Times story makes clear, almost everyone in and around the system that “processes” unaccompanied minors expects the children to work and figures that into their decisions.
Young people crossing the border are usually desperate to make money. They may owe thousands of dollars to smugglers who brought them here. They are risking everything with the goal of sending financial help to their endangered families. Their sponsors, who are often low-income people themselves, may expect the children they sponsor to contribute to their own upkeep. Some sponsors traffick the labor of migrant children, treating it like a business. On the other hand, school-age asylum seekers aren’t allowed to work legally because of “child protection” laws. This contradiction forces minors into the shadow economy and leaves them at the mercy of capitalism’s most unscrupulous profiteers.
And so there are thirteen-year-olds with fake IDs washing sheets in the back rooms of hotels, and exhausted fifteen-year-olds picking tomatoes all day in the sun or cleaning slaughterhouses with toxic chemicals all night. Young teenagers wait on the curb at day labor sites, competing for hard day labor in construction. As the Times story continues to reverberate nationally, we should be aware that thousands of unaccompanied child immigrants are living and working all around us in New York State. And we should always remember the local tragedy of Edwin Ajacalon, who migrated alone from Guatemala to Brooklyn at the age of 14. Edwin was riding his delivery bike in Brooklyn when he was mowed down by a speeding hit and run driver in a BMW. A whole family’s hopes suffered a huge blow with his death. The driver was never charged.
WHAT CAN WE DO?
- Demand that the Biden administration respect international law and let asylum-seeking families enter the US.
- Support basic income programs for unaccompanied minors, and all children without resources.
In solidarity and with collective care,
Jackson Heights Immigrant Solidarity Network (JHISN)
Follow @JHSolidarity on Facebook and Twitter and share this newsletter with friends, families, neighbors, networks, and colleagues so they can subscribe and receive news from JHISN.