Dear friends,
We approach the end of the harvest season, with All Hallow’s Eve, Dia de los Muertos (Day of the Dead), and Samhain each marking – for different cultures – a time of haunting, of remembrance, and of sacred darkness. In Queens County, at least 10,266 people have died from Covid since the start of the pandemic, many of them immigrants, all of them mourned. In this year’s mixed harvest of sorrow and loss, re-openings and return, we look for ways to both honor the dead and cultivate the dark seeds of renewal.
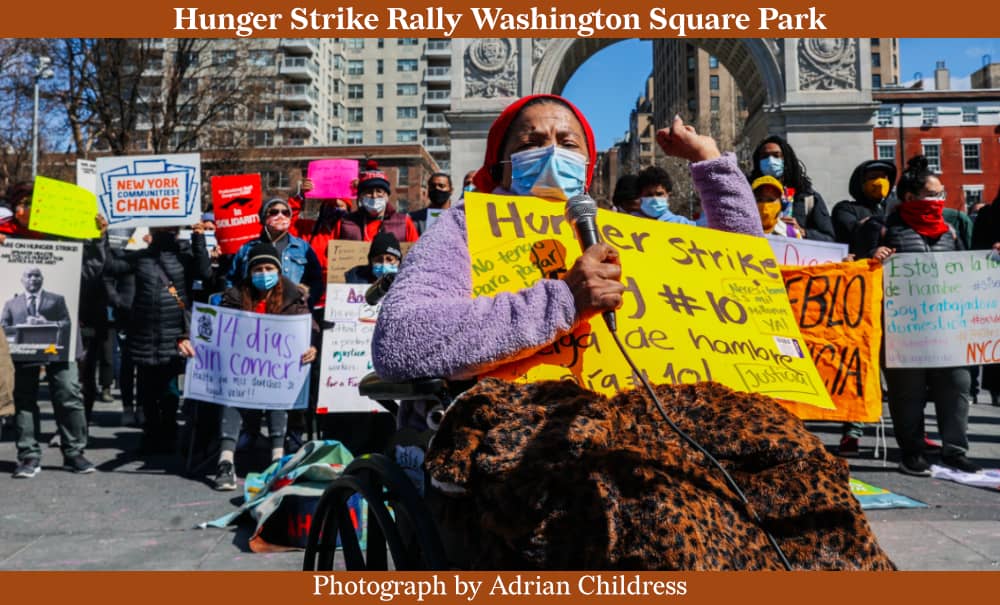
Our last newsletter reported on the 24/7 protest outside City Hall by immigrant taxi workers. Since then, workers have launched a hunger strike to demand relief from the medallion debt that is crushing NYC yellow cab drivers. To support the strikers, please consider a donation to the New York Taxi Workers Alliance.
In this issue, JHISN is excited to announce the launch of our crowdsourced Timeline of Immigrant Activism in Jackson Heights. You can help us build the story of our local history! We also offer an update on the 34th Avenue Open Street as it moves to become a permanent feature of the neighborhood.
Newsletter highlights:
- Interactive Digital Timeline of Immigrant Activism in Jackson Heights
- Keeping 34th Avenue an Open Street
1. Be Part of Our New Timeline of Local Immigrant Activism
JHISN works in solidarity with immigrants and their allies, disseminating information, and encouraging our neighbors to stand with, defend, and empower immigrants. We invite you to participate in our new online project, building a robust history of local immigrant activism. You can be part of this crowdsourced adventure of discovery and sharing which showcases activities that support and celebrate immigrant communities.
Did you know, for example, that Paola Mendoza has made a film, co-written a book, hosted a mourner’s walk, and curated an art installation all of which connect to immigrants in our neighborhoods? That the Latin American Integration Center (LAIC), established in Jackson Heights in 1992, was the precursor to Make the Road NY? Or that the majority of immigrant activist actions have been initiated by women in Queens?
To honor the contributions over the decades by many individuals and immigrant groups in Jackson Heights, Woodside, Corona, and nearby areas, JHISN has created the Timeline of Immigrant Activism. We seeded it with over 120 items: organizational foundings; changes in federal and state laws; marches and protests, including family-friendly events; academic and governmental publications, fiction and non-fiction accounts; and a range of artistic and cultural endeavors. Every one of these efforts is significant by itself. When we look at them collectively we can see the impressive picture of immigrant-led mobilizing and creativity that exists in this distinct part of Queens.
Did you know that, around 2010, the publication director of the Philippine Forum created a hyperlocal online news website for immigrant communities in Queens? It was named Queens7.com after the subway line that served the community.
JHISN is not an authority that knows all the details about these important events and activities. Our group is just a few years old, very young in comparison with groups that have organized here for decades. Many people in our neighborhood–you may be one of them since you subscribe to our newsletter–know a great deal more about these events and our local history. If you notice we have failed to include a march, or did not mention an important cultural event, or missed some important milestones, we encourage you to simply add an item to the timeline yourself.
Did you know that Adhikaar, CHHAYA CDC, and NICE (New Immigrant Community Empowerment) were part of the People’s Walking Tour in 2012, which later became a feature in the curriculum of a 2016 course on urban change at the University of Toronto?
The timeline is a crowdsourced initiative. Anyone can sign up to create an account and add items. There is a slight editorial review process because this topic is both significant and prone to flaring up arguments in public digital spaces. We seek to raise the voices of immigrants and those in solidarity with immigrant struggles by building this public archive. Submissions will be reviewed before they are made publicly available. As a small volunteer group, we ask for your patience, contributions, and collective memory as we build up this resource with you.
WHAT CAN WE DO?
- Share the link to the timeline jhimmigrantsolidarity.org/timeline with friends, colleagues, and others who can help it grow.
- Do your own research about local events and efforts and, when you locate something of importance to note or celebrate, search for it in the timeline. If it is missing, create an account and add the information.
- With every new item you add, you can also name one or more organizations that were involved. If the organization is not already on our list, you can add it. Just be sure to save your event description before you add the names of organizations.
2. DOT Plans for the 34th Avenue Open Street
Since May 2020, Jackson Heights residents have enjoyed the freedom of the 34th Avenue Open Street. Many organized activities have been held on the Avenue, including immigrant-led programming in the 90s and elsewhere along the new promenade. The Avenue was even named the “gold standard” for an Open Street. There has also been vocal opposition to a permanent Open Street, primarily from car owners as well as those concerned about the safety of pedestrians and children.
Representatives of the NYC Department of Transportation (DOT) finally unveiled a design proposal for 34th Avenue at Community Board 3 on October 21. More than 100 virtual participants attended the meeting. The DOT design was partly based on survey responses from more than 2000 local residents, including 90% of respondents who live in Jackson Heights.
The proposed design aims to reduce car traffic and incorporates significant input from the seven public schools on the Avenue. The design also takes note of how the Avenue has actually been used, and responds to some complaints received over the past year. The DOT slide presentation shows that the Open Street has in fact improved public safety: the total annual number of crashes and injuries along 34th Avenue has dropped since May 2020. The presentation also includes schematic representations of the design and introduces new vocabulary: diverters, chicane, plaza block, and shared space blocks.
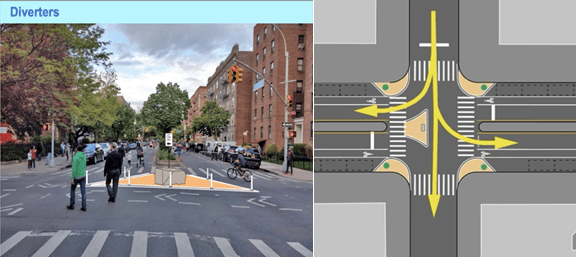
The key element of DOT’s proposal is the use of diverters (permanent triangular areas marked by paint, granite blocks, and planters) at all 26 intersections. These are designed to allow cars to turn onto 34th Avenue while preventing drivers from traveling more than one block without having to turn onto a side street. Diverters would replace the temporary metal barricades currently used, which are difficult to move, and which must be installed and removed every day. Here are schematics of a planned diverter and traffic flow around it:
In the DOT plan, there are four plaza blocks (car-free areas marked with paint and planters) on the north side of the Avenue. Two of them would be near PS 368 and IS 230. There would be a green marked bike path 4 feet from the median; the rest of the space would be set aside for pedestrians (see Slides 38 and 39). The plaza expands the pickup/drop-off area for the schools and allows for programming on the Avenue. The chicane (an offset curb extension to slow traffic) will slow any delivery vehicles.
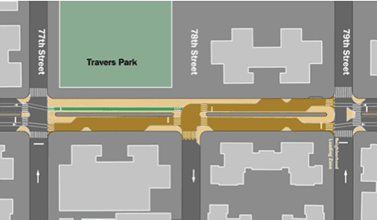
The area near Travers Park is slated to have a third plaza block at 77-78th streets and a shared space block at 78-79th streets, allowing access to residential buildings and more space for public events (see Slide 40).
The block near PS 212 (82-83rd streets) is planned to be a shared space block (see Slide 41). Since there has been little organized programming on 85-88th streets, they will simply have diverters at the intersections. Because of the apartment fire at 89th street, the final design for the avenue from 89th-92nd streets has been postponed.
From 93rd street to Junction Boulevard there is a fourth planned plaza block in front of PS 149, and a shared space block from 93rd to Junction Boulevard (see Slide 44). The bus stop on the west side of the street will be moved south.
There was a long Q&A period at the Community Board 3 meeting, with concerns raised about getting more feedback through door-to-door surveys, more traffic studies, sanitation issues, problems with Access-A-Ride, and the speed of motorcycles and mopeds on the Avenue.
DOT is accepting continued feedback on their design proposal through Fall and Winter 2021, with implementation anticipated for Spring 2022. Given the lack of green space or public commons in our primarily immigrant, working-class neighborhood, a permanent Open Street in Jackson Heights would be a huge and welcome transformation.
WHAT CAN WE DO?
- Review DOT’s slide presentation of the design proposal. Use the online form to send feedback to the DOT/Queens Borough Commissioner by selecting Open Streets as the General Topic. Then select “street or Sidewalk” to talk about a specific location or select “Citywide Concern” to make general feedback.
- Sign up for the 34th Avenue Open Streets Coalition monthly newsletter.
In solidarity and with collective care,
Jackson Heights Immigrant Solidarity Network (JHISN)
Follow @JHSolidarity on Facebook and Twitter and share this newsletter with friends, families, neighbors, networks, and colleagues so they can subscribe and receive news from JHISN.