Dear friends,
As the relentless bombing of homes, schools, refugee camps, mosques, churches, markets, hospitals, and humans in Gaza continues, we can only ask our readers to not turn away. For those who support an immediate ceasefire, see DRUM (Desis Rising Up & Moving) for local actions to pressure electeds. For broader NYC actions, please follow Jewish Voice for Peace NYC.
This week’s newsletter offers an update on a tentative agreement that would allow immigrant vendors to return to Corona Plaza. We then take a deeper look at the digital divide, in terms of both access and content, that excludes far too many asylum seekers and other migrants from full participation in online worlds.
Newsletter highlights:
- Deal for Corona Plaza street vendors?
- Digital access for immigrants to US
1. Return of Corona Plaza Vendors Linked to Soccer Stadium Approval
“I was calling a foul on the displacement of men and women who are hard workers, largely immigrants, in Corona Plaza who really deserve an opportunity to work”–Queens Borough President Donovan Richards on NY1
It’s been almost three months since street vendors at Corona Plaza–mostly immigrant women from Central and South America–were forced out by the Sanitation Department police. Ever since, vendors and their political allies have been urgently trying to make a deal with the Adams administration to reopen the Plaza and restore vendor livelihoods. Their proposals include limited, dedicated spaces for vendors to prevent overcrowding, while still retaining the “cultural spark” that the Plaza was known for. Although the administration has seemed willing to consider this in principle, they have dragged their feet.
Meanwhile, during this same period, the city has been working on securing final approvals for a new 25,000-seat soccer stadium at nearby Willets Point, expected to be ready for the New York City Football Club’s 2027 Major League Soccer season.
One of the needed approvals was that of vendor ally Borough President Donovan Richards, who had to okay changes to street maps. But early in October, Richards announced that he would not sign off until he secured an agreement allowing vendors to return to Corona Plaza, and also provide some of the vendors with space in the stadium’s concession operations.
“My position was and will continue to be, how are the local residents benefiting from this stadium? How’s the city treating the very community that this stadium is going to be placed? At the end of the day, this wasn’t about me, this wasn’t about politics, this was about largely immigrant women and children who were just trying to feed their families, who were just trying to pay their rent.” – Queens Borough President Donovan Richards
On October 16, Richards announced in an interview on NY1 that he had reached a tentative agreement to benefit the vendors and guarantee that the new jobs created will go to community members:
“We have reached a tentative agreement with the city now to get those vendors back on the site at Corona Plaza, and the goal is to ensure that…we create jobs. The stadium is a great project, but at the end of the day we have to make sure the benefits reach local communities.”
The return of vendors to the Plaza would affirm the importance of this lively food hub—for both workers and their customers.
WHAT CAN WE DO?
- Support Corona Plaza street vendors.
2. Unaddressed—the Digital Divide in NYC
Internet access is a key problem facing immigrants. Reduced access to adequate and appropriate digital services affects every step of migration, from border transit to legal proceedings to locating necessary services. Immigrant justice advocates, like the journalists of Documented NY, identified this serious obstacle by listening to the 5,700 members of their WhatsApp community, a third of whom are recently arrived asylum seekers.
Research from Cornell University has indicated that, while better digital tools could help immigrants, the content itself is often out of date and users worry their digital fingerprints may be tracked. This led an interdisciplinary team to create the Immigrant Rights for Health website, sharing “accurate and accessible information on health and legal benefits available to immigrants.”
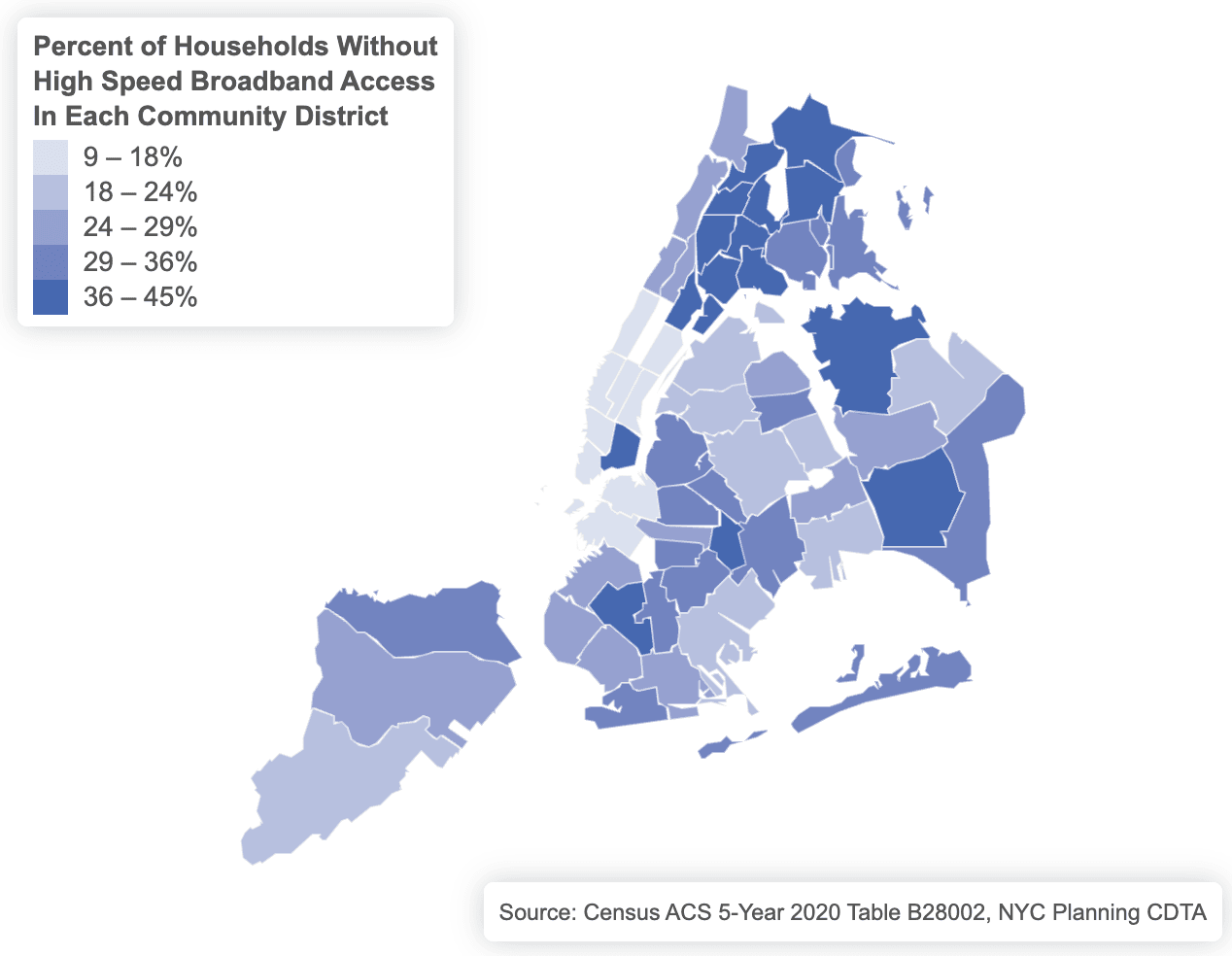
The existence of a digital divide hurts the people who are often most in need of internet access. This was a forefront issue during the pandemic years of lockdown from schools, work, and government/social services. In Jackson Heights, the city’s census review of 2020 found 26% of households lacked broadband connectivity. Mayor de Blasio’s Chief Technology Officer even created an Internet Master Plan to address the issue. The report acknowledged that around 1.5 million New Yorkers lacked an internet connection because a “private market solution to broadband service continues to leave out too many New Yorkers.” Two and a half years later, under Mayor Adams, the city quietly killed the Master Plan.
NYC Mesh identified this same internet access issue back in 2014. The volunteer-run, open-source, community broadband network aimed to create an affordable network controlled and operated by and for local residents as an alternative to the private market. NYC Mesh requires social trust to expand their open-source system which leverages the rooftops and households of its members, so its growth has always been hyper-local and limited.
The New York City Council made an initial effort during the pandemic to introduce local laws to improve network access. Its Committee on Technology introduced four local law proposals: 1) provide public school students with mobile hotspot devices; 2) create written materials on affordable internet programs; 3) provide public access to wireless networks; and 4) establish a website for cable franchise agreements. Although there were many positive conversations in Hearing Committees, where they even discussed options like providing network devices in shelters, all four initiatives since 2022 have been laid over in Committee—the bills were sent to the full Council for more debate and still await a final vote.
One program that has expanded is the city’s LinkNYC Public-Private Partnership which converted pay phones to internet access nodes. During 2023 Immigrant Heritage Week, the city and LinkNYC launched the “We Love Immigrant New York” campaign with the Mayor’s Office for Immigrant Affairs; it included a “We Speak NYC” program to help immigrants learn English. It also created the first Gigabit Center, at La Colmena in Staten Island, which was identified by Mayor Adams as a resource navigation center providing high-speed internet access for newly-arrived immigrants. A second Gigabit Center opened at Silicon Harlem in the Bronx in August 2023. There are also plans to bring network access to 200 NYCHA locations through the “Big Apple Connect,” though there is uncertainty as to how effective this will be.
In December 2022, a few months after southern states began busing immigrants to sanctuary cities, the American Immigration Council noted that 24% of immigrants were likely to lack broadband access. Comparatively, 20% of people born in the USA are without broadband. Housing those migrants in temporary shelters in NYC has highlighted this public issue; the New York City Bar reported in 2020 that the city needed to provide internet access to help people in temporary housing find permanent homes. In 2021, and again in 2023, they supported a state bill to do so. This has not yet become law but it has finally passed from the Senate to the Assembly.
For those making asylum claims, the need for network access is crucial. Most of our Newsletter readers will have heard about the CBP One phone app which has significantly, and by design, reduced applications for asylum because it creates a technology bottleneck. Even people who can get access to devices are not guaranteed access to service. Once in the US, continued access will be needed not just for information, but to attend online court proceedings where many cases are now heard.
In closing, it is noteworthy that most of the research and discussion, even for global digital access initiatives like the UN Secretary-General’s Roadmap for Digital Cooperation, has not been updated much since 2022. Clayton Banks, who co-founded Silicon Harlem, summed up the stalled efforts to change the digital divide: “The city put over $160 million in the [2020] budget to make this happen, but not a nickel of it was spent.“
WHAT CAN WE DO?
- Contact your NYS Assemblyperson to support Assembly Bill A5649A guaranteeing internet access for all people in temporary housing.
In solidarity and with collective care,
Jackson Heights Immigrant Solidarity Network (JHISN)
Follow @JHSolidarity on Facebook and Twitter and share this newsletter with friends, families, neighbors, networks, and colleagues so they can subscribe and receive news from JHISN.